
Kidney injury molecule-1, neutrophil gelatinase–associated lipocalin, tumor-necrotizing factor-α, transforming growth factor-β, tissue total oxidant status, and total antioxidant status levels were measured in kidney homogenates 3 and 24 h after decompression. Crush injury was induced by 6 h of direct compression to both hindlimbs of anesthetized rats with blocks weighing 3.6 kg each sides, followed by 3 or 24 h of decompression. All these groups were also separated as 3 and 24 h after decompression. Rats were divided into six groups (n = 8): Sham (steril saline ip), crush (sterile saline ip), crush + NaHS (sodium hydrosulfide, an H2S donor) (100 μmol/kg ip). In this study, effects of H2S on kidney injury were investigated in a rat model of crush syndrome. It is involved in homeostatic functions, such as blood pressure control, apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an endogenously produced gaseous signaling molecule. If there is no alternative other than prolonged field care, the medical community must be prepared to offer health care and even perform dialysis in austere conditions, which in that case, is the only option to decrease the death toll resulting from AKI.Īcute kidney injury is the most serious complication of crush syndrome. Other man-made disasters also may cause AKI however, the number of patients is mostly lower and treatment possibilities are broader than in war. Transporting casualties initially to field hospitals, and afterward to higher-level health care facilities at the earliest convenience, is critical. Measures for decreasing the risk of AKI include making preparations for foreseeable disasters, and early management of polytrauma-related complications, hypovolemia, and other pathogenetic mechanisms.
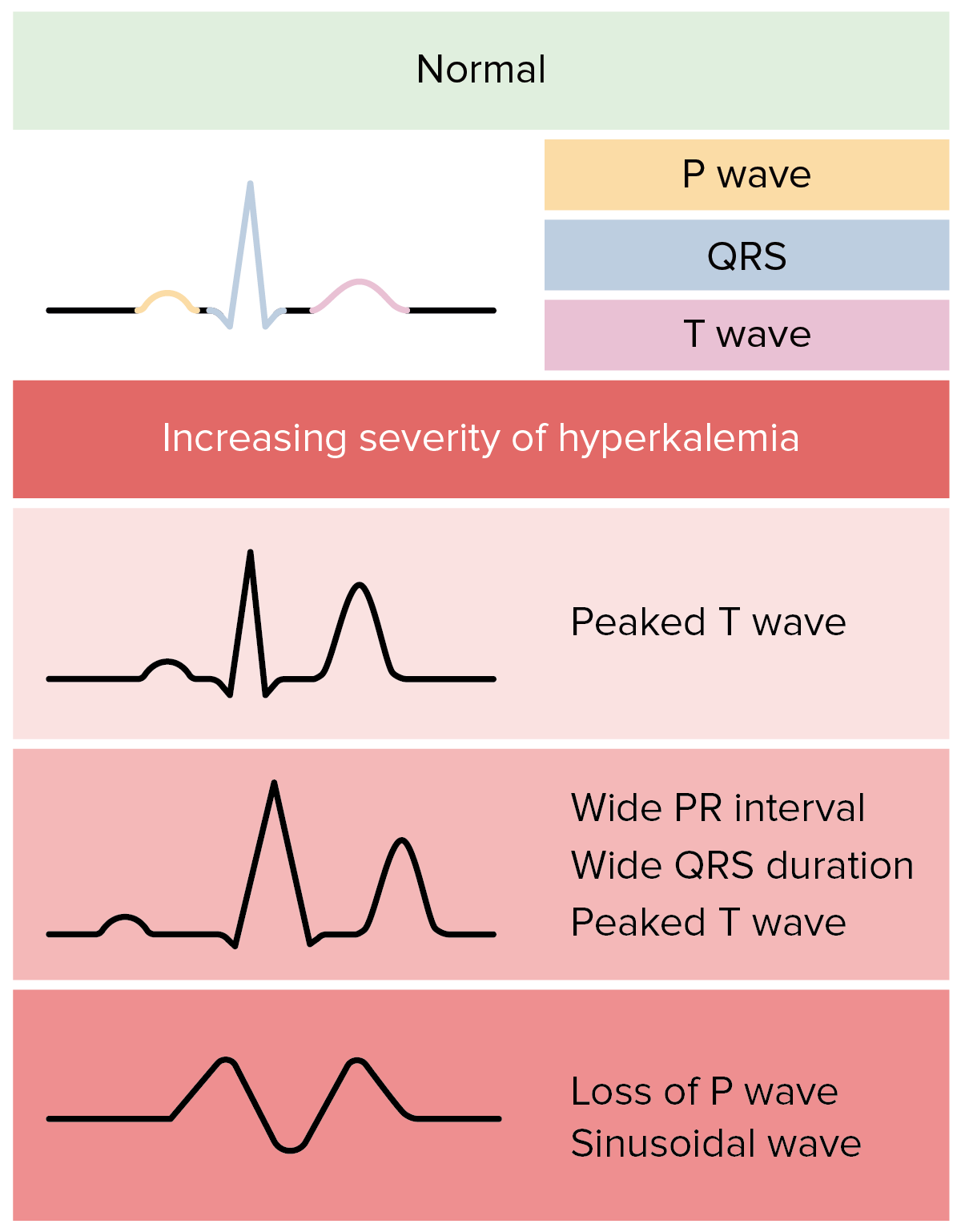
The prognosis usually is unfavorable because of systemic and polytrauma-related complications and suboptimal therapeutic interventions. Thus, prerenal, intrinsic renal, or postrenal AKI may develop at the battlefield, in field hospitals, or tertiary care centers, resulting not only from traumatic, but also nontraumatic, etiologies.

War-related AKI may develop as a result of polytrauma, traumatic bleeding and hypovolemia, chemical and airborne toxin exposure, and crush syndrome.
#Hyperkalemia ecg findings Activator#
The Nrf2 activator BM reversed the crush-induced changes in the experimental rats.īM treatment prevented the progression of crush-related AKI in rats possibly through its cytoprotective effects of being an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic agent.Īcute kidney injury (AKI) is frequent during wars and other man-made disasters, and contributes significantly to the overall death toll. BM treatment decreased apoptosis in crush-related AKI. Serum CK, BUN and creatinine concentrations were also reduced with BM. Apoptosis was assessed using the TUNEL method.īM treatment reduced KIM-1, NGAL, TNF-α, TGF-β1, TOS concentrations, and increased TAS concentrations in the kidneys 3 and 24 h after decompression. Bcl-2 was measured using immunohistochemistry. Glomerular and tubular structures were examined histopathologically. Serum creatine kinase (CK), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine concentrations were also measured. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), tumor necrotizing factor-α (TNF-α), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) concentrations, tissue total oxidant status (TOS) and total antioxidant status (TAS) were measured in the kidneys. Crush injury was induced by 6 h of direct compression to both hind limbs of the rats with blocks weighing 3.6 kg on each side, followed by 3 and 24 h of decompression. All groups were also divided as 3 and 24 h after decompression. Sixty-four rats were separated equally into eight groups, sham (sterile saline ip), crush, crush + vehicle (DMSO ip), and crush + BM (10 mg/kg ip) (n = 8). The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of bardoxolone methyl (BM), a nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activator, on acute kidney injury in a rat model of crush syndrome model.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
